-
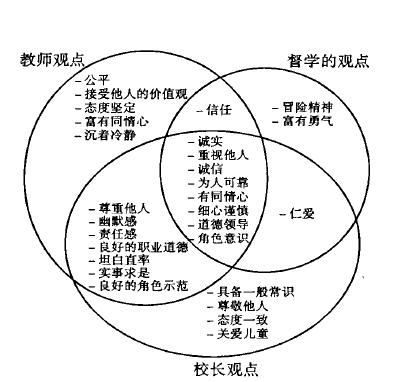
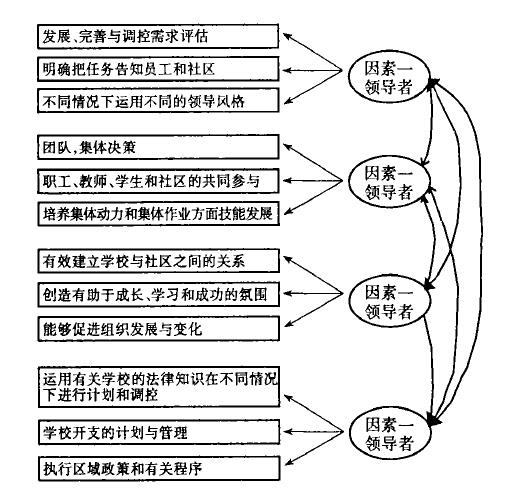
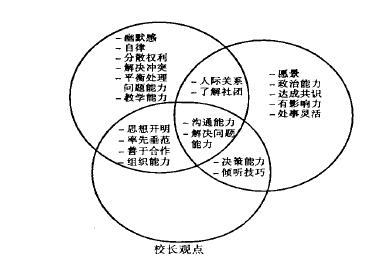
摘要: 本文探讨了在现场管理和学校重建的过程中,教师、校长和督学三方对领导角色看法的相同和不同之处。文章从定量研究和定性研究的实际操作出发,从知识技能和价值观三方面总结出了领导理论的二因素模式和四因素模式,并探讨了两种模式之间的关系。
-
表 1 教师、校长和督导各自所提及的领导应具备的最重要的能力、知识和价值观方面内容的频率
表 2 接受检验的二因素领导模式和四因素领导模式中的吻合指数
-
[1] B.M.Bass(1990).Bass & Stogdill's handbook of leadership : Theory, research, and managerial applications.New York : Free Press. [2] B.M.Bass & B.J.Avolio(1994).Improving organizational effectiveness through transformational leadership.Thousand Oaks : Sage Publications. [3] R.R.Blake & J.S.Mouton(1985).The Managerial Grid III.Houston : Gulf. [4] H.Boles & J.Davenport(1975).Introduction to educational leadership.New York : Harper & Row Publishers. [5] L.C.Bolman & T.E.Deal(1991).Reframing organizations.San Francisco, CA : Jossey -Bass. [6] M.W.Browne & R.Cudeck(1993).Alternative ways of assessing model fit.In K.A.Bollen & J.S.Long (Eds.).Testing struc-tural equation models (pp.136 -162).Newbury Park, CA : Sage. [7] Burns (1978).Leadership.New York : Harper Torchbooks. [8] J.M.Burns(1978).Leadership.New Work : Harper & Row. [9] T.Bush & L.Bell(1995).The principals and practice of educational management.London : Paul Chapman Publishing. [10] R.V.Carlson(1996).Reframing and reform : Perspectives on organization, leadership, and school change.White Plains, NY : Long-man. [11] D.Cartwright & A.Zander(1960).Group dynamics : Research and theory (2nd ed.).Evanston, Ill.: Row, Peterson. [12] J.Cohen(1960).A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales.Educational and Psychological Measurement, 20(1), 37 -46. [13] CCSSO (Council of Chief State School Officers)(1996).Interstate School Leaders Licensure Consortium : Standardsfor school leaders.Washington, DC : Author. [14] R.P.Craig & C.J.Norris(1991).Values perception and future educational leaders.Journal of School Leadership, 1(3), 222 -234. [15] L.Crocker & J.Algina(1986).Introduction to classical and modern test theory.Orlando FL: Holt, Rinehart and Winston, Inc. [16] R.Cudeck & M.W.Browne(1983).Cross -validation of covariance structures.Multivariate Behavioral Research, 18, 147 -167. [17] R.L.Daft(1994).Management (3rd ed.).Florida : Harcourt Brace College Publishers. [18] J.C.Daresh(1994).Restructuring educational leadership preparation : Identify needed conditions.Journal of School Leadership, 4 (1), 28 -38. [19] S.H.Davis(1998, November).Taking aim at effective leadership.Thrust for Educational Leadership, 6-9. [20] T.E.Deal & A.Kennedy(1982).Corporate cultures : The rites and rituals of corporate life.Reading, MA : Addison -Wesley. [21] M.DePree(1989).Leadership is an art.New York : Doubleday. [22] R.F.Elmore(2000).Building a new structure for school leadership.The Albert Shanker Institute, 1 -39. [23] M.G.Evans(1970).The effects of supervisory behavior on the path -goal relationship.Organizational Behavior and Human Perfor-mance 5, 277-298. [24] F.E.Fiedler(1967).A theory of leadership effectiveness.New York : McGraw -Hill. [25] D.Goleman, R.Boyatzis, A.McKee(2002).Primal leadership : Realizing the power of emotional intelligence.Boston : Harvard Busi-ness School Press. [26] J.I.Goodlad, R.Soder & K.A.Sirotnik(Eds.).(1990).The moral dimensions of teaching.San Francisco, CA : Jossey -Bass. [27] P.L.Grossman(1990).The making of a teacher : Teacher knowledge and teacher education.New York : Teachers College Press. [28] P.Hersey & K.Blanchard(1974).So you want to know your leadership style?Training and Development Journal, 6. [29] P.Hersey, K.H.Blanchard & D.E.Johnson(1996).Management of organizational behavior: utilizing human resources.Upper Saddle River, NJ : Prentice Hall. [30] C.Hodgkinson(1991).Educational leadership : The moral art.Albany : State University of New York Press. [31] R.J.House & T.R.Mitchell(1974).Path -Goal Theory of leadership.Journal of Contemporary Business. [32] W.K.Hoy & A.E.Woolfolk(1990).Socialization of student teachers.American Educational Research Journal, 27 (2), 279 -300. [33] C.Hsieh & J.Shen(1998).Teachers, principal's and superintendents' conceptions of leadership.S chool Leadership & Management, 18 (1), 107 -121. [34] R.Kahn(1979).Psicologia social de las organizaciones.Social psicology in organizations.Mexico : Editorial Trillas. [35] T.J.Kalliath, A.C.Bluedorn & D.F.Gillespie(1999, February).A Confirmatory factor analysisof the competing values instrument.Educational and Psychological Measurement, 59 (1), 143 -158. [36] D.Katz & R.Kahn(1952).Some Recent Findings in Human Relations.In E.Swanson, T.Newcomb, & E.Hartley (Eds.), Read-ings in Social Psychology.New York : Holt, Reinhart, and Winston. [37] R.Kelley(1992).The power of followership.New York : Currency and Doubleday. [38] H.Kerzner(1997).Project management.A systems approach to planning, scheduling, and controlling (6th ed.).Canada: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. [39] K.Lewin, R.Lippitt & R.K.White(1939).Patterns of aggressive behavior in experimentally created social climates.Journal of Social Psychology, 10, 271-301. [40] R.Likert(1961).New patterns of management.New York : McGraw -Hill. [41] R.Likert(1967).The Human Organization.New York : McGraw -Hill. [42] R.Likert(1979).From production —and employee—centeredness to Systems 1 -4.Journal of Management, 5, 147 -156. [43] B.Malen(1994).Enacting site -based management : A political utilities analysis.Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis, 16(3), 249 -267. [44] D.L.Morgan(1988).Focus groups as qualitative research.Newbury, CA : Sage. [45] F.M.Newmann, B.Smith, E.L.Allensworth & A.Bryk(2001)Instructional program coherence : What it is and why it should guide school improvement policy.Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis, 23 (4), 297 -321. [46] C.C.Phillips(2000).Issues of factorial invariance inherent in conceptual change : Teacher's evolving perceptions of classroom prac-tice.Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Western Michigan University, Michigan. [47] L.Rodríguez -Campos(2002).The structure of the leadership construct : A test of factorial invariance using structural equation model-ing.Doctoral dissertation, Western Michigan University, Michigan. [48] C.Schriesheim & J.Bird(1979).Contributions of the Ohio State studies to the field of leadership.Journal of Management, 5, 135 -145. [49] R.E.Schumacker & R.G.Lomax(1996).A beginner'sguide to structural equation modeling.Mahwah, NJ : Lawrence Erlbaum Asso-ciates, Publishers. [50] P.M.Senge(1990).The fifth discipline: The art and practice of the learning organization.Broadway, NY : Publishing Group, Inc. [51] C.L.Shartle(1979).Early years of the Ohio State University Leadership Studies.Journal of Management, 5, 126 -134. [52] J.Shen(1993)." Teaching as a moral enterprise" revisited.Review of Education, 15 (3 -4), 333 -339. [53] J.Shen(2001).Teacher and principal empowerment : national, longitudinal, and comparative perspectives.Educational Horizons, 79 (3), 124-129. [54] J.Shen(2005).Principal'and teachers'power.In Shen, J.et al., School principals (pp.106-116).New York : Peter Lang Pub-lishing. [55] R.Soder(2001).The language of leadership.San Francisco : Jossey -Bass. [56] J.P.Spillane R.Halverson & J.B.Diamond(2001).Investigating school leadership practice: A distributed perspective.Educational Researcher, 30 (3), 23-28. [57] R.G.Stakenas(1994).Program reform in administrator preparation : The process of change.NASSP Bulletin, 78(559), 28 -32. [58] D.W.Stewart & P.N.Shamdasani(1990).Focus groups : Theory and practice.Newbury Park, CA : Sage. [59] R.M.Stogdill & C.L.Shartle(1955).Methods in the study of administrative leadership.Columbus, OH : Bureau of Business Re-search, College of Commerce and Administration. [60] R.Tannenbaum & W.H.Schmidt(1973).How to choose a leadership pattern.Harvard Business Review. [61] S.D.Thomson(1992).National standards for school administrators.International Journal of Educational Reform, 1(1), 54 -58. [62] V.Vroom(1976).Can leaders learn to lead?Organizational Dynamics, 4. [63] C.H.Weiss & J.Cambone(1994).Principals, shared decision making, and school reform.Educational Evaluation and Policy Analy-sis, 16(3), 287 -301. [64] K.F.Widaman & S.P.Reise(1997).Exploring the measurement invariance of psychological instruments : [65] Applications in the substance abuse domain.In K.J.Bryant, M.Windle & S.G.West (Eds.), The science of prevention : Method-ological advances from alcohol and substance abuse research (pp.281 -324).Washington, DC : American Psychological Association. [66] P.Wohlstetter, R.Smyer & S.A.Mohrman(1994).New boundaries for school -based management : The high involvement model.Ed-ucational Evaluation and Policy Analysis, 16(3), 268-286. -





 下载:
下载: