Identifying the “Best Evidence”: How to Use Meta-analysis to Conduct a Literature Review—A Case of STEM Education’s Effect on Students’ Academic Achievement
-
摘要: 元分析相对于传统的主观性文献综述方法而言,能够更加有效、客观和规范地从既有实证研究文献中梳理出一般性、规律性的结论,因此成为教育循证改革过程中寻找"最佳证据"的重要方法。与国外相比,我国运用元分析方法进行实证文献综述的研究还比较少。针对于此,本研究以STEM教育对学生学业成绩的影响为例,展示了运用元分析方法进行实证研究综述的过程。研究发现STEM教育有利于提高学生的学业成绩(d=0.410),STEM教育方法、受教育阶段、地区和样本量等因素均会显著影响到STEM教育的效果。这样的研究,不仅提供了关于STEM教育效果的一般性证据,而且在方法层面探讨了如何通过文献综述获得可靠证据以支持教育改革。Abstract: Compared with the method of traditional subjective literature review, meta-analysis is more objective, normative, and can effectively sort out general conclusion from existing empirical researches. Therefore, it has become an important method to identify the “best evidence” in the process of evidence-based educational reform. So far there are few educational studies in China using the meta-analysis method to review the empirical literatures. In view of this, this research analyzes the impact of STEM education on students’ academic achievement as an example of how to use meta-analysis to synthesise existing empirical research. We found: 1) STEM education is conductive to students academic achievements (d=0.410); 2) factors like educational methods, students’ educational stage, location and sample size can affect the effects. The study provides the general evidence of effects of STEM education and explores how to obtain reliable evidence through a literature review to support educational reform.
-
Key words:
- evidence-based educational reform /
- STEM education /
- academic achievement /
- meta-analysis
-
表 1 STEM教育领域内元分析研究的基本信息
作者 研究内容 合并效应量 调节变量 时间范围 纳入研究的数量 Belland
et al.(2017)STEM教育中支架式
学习的效果未报告 受教育阶段、学生特征、教学方法、
学科、测评水平未报告 56 Steenbergen-Hu & Cooper(2013) 智能教学系统(ITS)在数学
学习中的效果未校正g=0.090
校正g=0.010学科、干预时长、学生特征、受教育阶段、样本量、研究设计、数据收集的年份、文献类型、测试时间、测试类型 1997—2010 26 An(2012) STEM项目实施评估 参与度d=0.346
效果d=0.456
延续性d=0.369研究设计、项目特征、受教育阶段、
地区、文献年份、1980—2010 91 Carbonneau
et al.(2013)实体教具在数学教学中的效果 d=0.370 文献是否发表、研究设计、教具使用者、测试类型、独立性、教具说明、
学科、干预时长2010—2011 55 Yasin & Yunus(2014) 技术与工程教育中旨在培养创新能力的教学方法的效果 d=1.020 教学方法、受教育阶段 2000—2012 16 Kalaian & Kasim(2014) 小组学习对学生统计学知识的影响 0.600 文献年份、研究设计、教学方法、干预时长、是否使用电脑、教师类型、测试类型、样本量受教育阶段、地区、 1990—2009 9 Belland
et al.(2015)STEM教育中支架式学习的效果 g=0.530 支架式特征、研究方法特征、
测评水平、有效性未报告 7 Freeman
et al.(2014)活动式学习在STEM教育中的效果 d=0.470 OR=1.950 学科、测试项目、班级规模、研究设计 1998—2010 225 Young
et al.(2017)校外STEM项目对学生STEM兴趣的影响 d=0.370 校外项目类型、受教育阶段、校外项目的目的、性别、种族、研究质量 2009—2015 19 Yildirim(2016) STEM教育对学生成绩和能力的影响 未报告 未报告 1996—2016 33 Kim et al.(2018) 问题式教学背景下支架式学习的效果 g=0.385 高阶认知能力的类型、支架式定制、支架式学习的特征、学科 1990—2015 21 Kalaian
et al.(2018)小组学习在工程和技术教育上中的效果 g=0.450 文献年份、文献类型、研究设计、受教育阶段、地区、学科 1995—2010 18 Becker & Park(2011) STEM整合方法对学生的影响 d=0.630 受教育阶段、STEM整合方法的
类型、学科1989—2009 28 Apugliese & Lewis(2017) 合作学习对学生化学学科理解的影响 g=0.680 评估类型、评估范围、合作学习的
使用途径、小组规模2001—2015 24 Michko(2008) 技术教育与工程教育整合的效果 g=0.433 未报告 1996—2005 45 Sarac(2018) STEM教育对学生成就的影响 成绩d=0.442
态度d=0.620
技能d=0.820文献类型、学科、受教育阶段、 2010—2017 成绩27
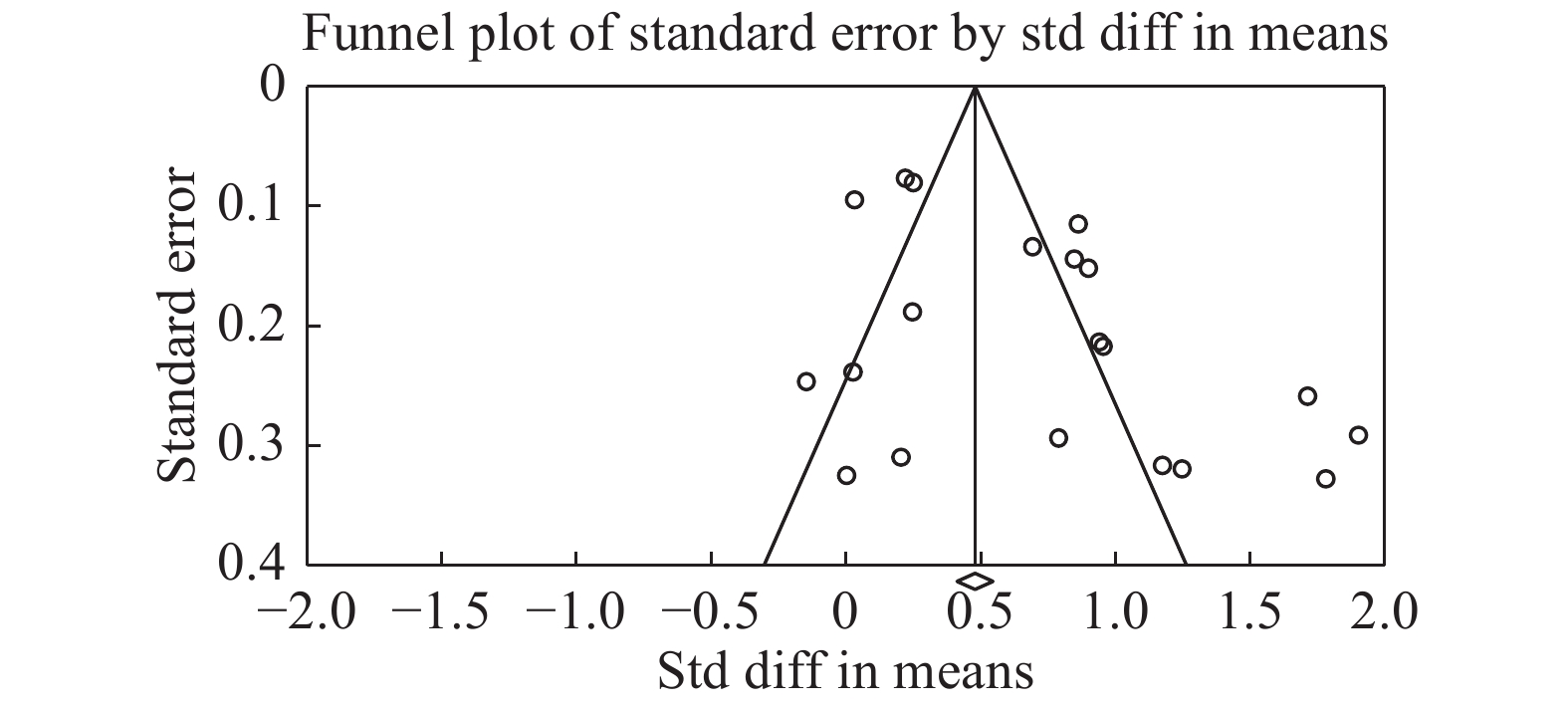
态度18
技能13Sokolowski(2013) 探索性学习环境对学生数学成就的影响 0.530 干预时长、教学模式、受教育阶段、
内容标准2000—2012 13 Sokolowski
et al.(2015)使用探索式计算机环境在数学教育中的效果 g=0.600 受教育阶段、教学工具、干预时长、
学科、学习设定类型2000—2013 24 注:“未报告”表示文章未给出表格所列内容的相关信息;合并效应量一栏中纯数值表示文章未给出效应量的类型。 表 2 纳入文献的信息
文献 Ge SES E Gr D L I Rd Ss Barth,2013 B M W P Science U.S. STEM integration QE S(66) Ojaleye & Awofala,2018 B U U H Mathematics Nigeria pbl QE S(212) Fatade,et al.,2013 B U U H Mathematics Nigeria pbl QE S(96) Maxwell,et al.,2015 B V V P Science U.S. IBL QE S(42) Rehmat,2015 B V V P Science U.S. pbl QE S(98) Fan & Yu,2015 B U U H Engineering Taiwan,China STEM integration QE L(332) Harris,et al.,2015a B U V H Science U.S. PBL RE L(757) Harris,et al.,2015b B U V H Science U.S. PBL RE L(654) Merrill,2001 U U U H Science U.S. STEM integration QE S(71) Kim,et al.,2012 B L V H Science U.S. IBL QE S(115) Holveck,2012 B V V M Science U.S. IBL QE L(474) Araz,2007 U M U P Science Turkey pbl QE S(192) Kizkapan & Bektas,2017 B U U M Science Turkey PBL QE S(38) Kassir,2013 B U U P Science United Arabs Emirates IBL QE S(52) Robinson,et al.,2014a U L U P Science U.S. IBL RE S(78) Robinson,et al.,2014b U L U P Science U.S. IBL RE S(82) Cotabish,et al.,2013 U U U P Science U.S. IBL RE S(239) Akinoglu & Tandogan,2007 B U U M Science Turkey pbl QE S(50) Acar,et al.,2018a U U U P Science Turkey STEM integration QE S(47) Acar,et al,2018b U U U P Mathematics Turkey STEM integration QE S(47) 表 3 文献效应量及合并效应量
文献 学科 统计信息 Cohen’d SE Variance Lower limit Upper limit Z-value p-value Barth,2013 Science −0.147 0.247 0.061 −0.630 0.336 −0.596 0.551 Ojaleye & Awofala,2018 Mathematics 0.847 0.144 0.021 0.565 1.130 5.885 <0.0001 Fatade,et al.,2013 Mathematics 0.955 0.217 0.047 0.529 1.380 4.400 <0.0001 Maxwell,et al.,2015 Science 0.204 0.310 0.096 −0.403 0.811 0.659 0.510 Rehmat,2015 Science 0.940 0.213 0.045 0.522 1.358 4.409 <0.0001 Fan & Yu,2015 Engineering 0.862 0.115 0.013 0.637 1.087 7.507 <0.0001 Harris,et al.,2015a Science 0.220 0.076 0.006 0.070 0.370 2.879 0.004 Harris,et al.,2015b Science 0.250 0.080 0.006 0.093 0.407 3.119 0.002 Merrill,2001 Science 0.026 0.239 0.057 −0.442 0.493 0.109 0.913 Kim,et al.,2012 Science 0.247 0.188 0.035 −0.122 0.615 1.312 0.189 Holveck,2012 Science 0.031 0.095 0.009 −0.154 0.217 0.331 0.741 Araz,2007 Science 0.899 0.152 0.023 0.602 1.197 5.930 <0.0001 Kizkapan & Bektas,2017 Science 0.002 0.325 0.106 −0.635 0.639 0.006 0.995 Kassir,2013 Science 1.781 0.328 0.107 1.138 2.423 5.433 <0.0001 Robinson,et al.,2014a Science 1.902 0.291 0.085 1.311 2.473 6.530 <0.0001 Robinson,et al.,2014b Science 1.713 0.259 0.067 1.206 2.220 6.621 <0.0001 Cotabish,et al.,2013 Science 0.693 0.134 0.018 0.431 0.955 5.184 <0.0001 Akinoglu & Tandogan,2007 Science 0.789 0.294 0.086 0.214 1.365 2.687 0.007 Acar,et al.,2018a Science 1.247 0.319 0.102 0.621 1.873 3.905 <0.0001 Acar,et al,2018b Mathematics 1.174 0.316 0.100 0.554 1.795 3.711 <0.0001 合并效应量 0.700 0.111 0.012 0.483 0.918 6.316 <0.0001 表 4 调节变量的选取及其分类
调节变量类别 调节变量内容 研究特征 研究设计、样本特征、样本量、测试工具、测试项目、地区、干预时长 干预特征 STEM教育方法、学科、受教育阶段 文献特征 文献年份、文献类型 表 5 调节效应分析
调节变量 K QB ES 95% CI p-value STEM教育方法 PBL 3 47.760(p<0.0001) 0.228 0.121 0.335 <0.0001 pbl 5 0.888 0.726 1.050 <0.0001 IBL 7 0.907 0.362 1.453 0.001 STEM integration 5 0.614 0.094 1.134 <0.0001 受教育阶段 小学 10 8.287(p=0.016) 1.021 0.659 1.384 <0.0001 初中 3 0.237 −0.225 0.699 0.315 高中 7 0.487 0.229 0.745 <0.0001 学科 科学 16 2.975(p=0.226) 0.638 0.391 0.885 <0.0001 数学 3 0.917 0.697 1.137 <0.0001 工程 1 0.862 0.637 1.087 <0.0001 地区 美国 11 14.022(p=0.007) 0.515 0.248 0.781 <0.0001 中国台湾 1 0.862 0.637 1.087 <0.0001 土耳其 5 0.834 0.468 1.119 <0.0001 尼日利亚 2 0.880 0.645 1.115 <0.0001 阿联酋 1 1.781 1.138 2.423 <0.0001 研究设计 准实验 15 0.743(p=0.389) 0.643 0.380 0.905 <0.0001 随机实验 5 0.871 0.422 1.320 <0.0001 干预时长 0—2月 5 8.006(p=0.091) 0.253 −0.172 0.677 0.244 2—4月 4 0.865 0.708 1.021 <0.0001 4—6月 3 1.066 0.535 1.597 <0.0001 6月以上 5 0.787 0.327 1.246 0.001 未报告 3 0.741 −0.213 1.695 0.128 测试工具 标准化测试 3 0.002(p=0.964) 0.722 −0.198 1.643 0.124 非标准化测试 17 0.701 0.471 0.931 <0.0001 样本量 大样本 4 5.782(p=0.016) 0.333 0.040 0.626 0.026 小样本 16 0.816 0.553 1.079 <0.0001 文献年份 1996—2007 3 0.208(p=0.648) 0.582 0.022 1.139 0.041 2007至今 17 0.722 0.483 0.962 <0.0001 文献类型 期刊 15 0.020(p=0.887) 0.716 0.475 0.957 <0.0001 非期刊 5 0.670 0.085 1.255 0.205 -
[1] 卢谢峰, 唐源鸿, 曾凡梅. (2011). 效应量: 估计、报告和解释. 心理学探新,31(3),260−264. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5184.2011.03.014 [2] 姚计海. (2017). “文献法”是研究方法吗?——兼谈研究整合法. 国家教育行政学院学报,19(7),89−94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4038.2017.07.014 [3] 张斌贤, 李曙光. (2015). 文献综述与教育学博士学位论文撰写. 学位与研究生教育,32(1),59−63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-960X.2015.01.022 [4] 张天嵩, 董圣杰, 周支瑞. (2015). 高级Meta分析方法——基于Stata实现. 上海: 复旦大学出版社. [5] Acar, D., Tertemiz, N., & Tasdemir, A. (2018). The Effects of STEM Training on the Academic Achievement of 4th Graders in Science and Mathematics and their Views on STEM Training Teachers. International Electronic Journal of Elementary Education, 10(4), 505−513. [6] Akinoglu, O., & Tandogan, R. O. (2007). The Effects of Problem-Based Active Learning in Science Education on Students’ Academic Achievement, Attitude and Concept Learning. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science & Technology Education, 3(1), 71−81. [7] An, D. (2012). A Meta-Analysis of the Effectiveness of STEM-Programs in the United States. Seoul: Sangmyung University. [8] Apugliese, A., & Lewis, S. T. (2017). Impact of instructional decisions on the effectiveness of cooperative learning in chemistry through meta-analysis. Chemistry Education Research and Practice, 18, 271−278. doi: 10.1039/C6RP00195E [9] Araz, G. (2007). The Effect of Problem-Based Learning on the Elementary School Students' Achievement in Genetics. Department of Elementary Science and Mathematics Education. [10] Atkinson, R. D., & Mayo, M. J. (2010). Refueling the US Innovation Economy: Fresh Approaches to Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) Education. The Information Technology & Innovation Foundation. [11] Barth, K. N. (2013). An Investigation of the Effects of Integrating Science and Engineering Content and Pedagogy in an Elementary School Classroom (Doctoral dissertation). Provo: Brigham Young University. [12] Becker, K., & Park, K. (2011). Integrative Approaches among Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) Subjects on Students' Learning: A Meta-Analysis. Journal of STEM Education: Innovations and Research, 12(5), 23−37. [13] Bediou, B., Adams, D. M., Mayer, R. E., Tipton, E., & Green, C. S. (2018). Meta- Analysis of Action Video Game Impact on Perceptual, Attentional, and Cognitive Skills. Psychological Bulletin, 144(1), 77−110. doi: 10.1037/bul0000130 [14] Belland, B. R., Walker, A. E., Olsen, M. W., & Leary, H. (2015). A Pilot Meta-Analysis of Computer-Based Scaffolding in STEM Education. Educational Technology & Society, 18(1), 183−197. [15] Belland, B. R., Walker, A. E., & Kim, N. J. (2017). A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis to Synthesize the Influence of Contexts of Scaffolding Use on Cognitive Outcomes in STEM Education. Review of Educational Research, 87(6), 1042−1081. doi: 10.3102/0034654317723009 [16] Bicer, A., Navruz, B., Capraro, R. M., Capraro, M. M., Oner, T., & Boedeker, P. (2015). STEM Schools VS. Non-STEM Schools: Comparing Students’ Mathematics Growth Rate on High-Stakes Test Performance. International Journal on New Trends in Education and Their Implications, 6(1), 138−150. [17] Bicer, A., Capraro, R. M., & Capraro, M. M. (2017). Integrated STEM Assessment Model. EURASIA Journal of Mathematics, Science & Technology Education, 13(7), 3959−3968. [18] Borenstein, M., Hedges, L. V., Higgins, J. P. T., & Rothstein, H. R. (2009). Introduction to Meta-Analysis. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. [19] Cakici, Y., & Turkmen, N. (2013). An Investigation of the Effect of Project-Based Learning Approach on Children’s Achievement and Attitude in Science. The Online Journal of Science and Technology, 3(2), 10−17. [20] Carbonneau, K. J., Marley, S. C., Selig, J. P. (2013). A Meta-Analysis of the Efficacy of Teaching Mathematics With Concrete Manipulatives. Journal of Educational Psychology, 105(2), 380−400. doi: 10.1037/a0031084 [21] Carmichael, C. C. (2017). A State-By-State Policy Analysis of STEM Education for K-12 Public Schools (Ed.D. Dissertation). New Jersey: Seton Hall University. [22] Cervetii, G. N., Barber, J., Dorph, R., Pearson, D., & Goldschmidt, P. G. (2012). The Impact of an Integrated Approach to Science and Literacy in Elementary School Classrooms. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 19(5), 631−658. [23] Cheung, A., & Slavin, R. E. (2012). Effects of Educational Technology Applications on Reading Outcomes for Struggling Readers: A Best Evidence Synthesis. Center for Research and Reform in Education, Johns Hopkins University. [24] Cheung, A., & Slavin, R. E. (2013a). The Effectiveness of Educational Technology Applications on Mathematics Achievement in K-12 Classrooms: A meta-analysis. Educational Research Review, 9(1), 88−11. [25] Cheung, A. C. K., & Slavin, R. E. (2013b). Effects of Educational Technology Applications on Reading Outcomes for Struggling Readers: A Best Evidence Synthesis. Reading Research Quarterly, 48(3), 277−299. doi: 10.1002/rrq.50 [26] Cheung, A., & Slavin, R. E. (2016). How Methodological Features Affect Effect Sizes in Education. Educational Researcher, 45(5), 283−292. doi: 10.3102/0013189X16656615 [27] Chow, S. L. (1988). Significance Test or Effect Size?. Psychological Bulletin, 103(1), 105−110. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.103.1.105 [28] Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences (2nd ed.). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum. [29] Cotabish, A., Dailey, D., Robinson, A., & Hughes, G. (2013). The Effects of a STEM Intervention on Elementary Students’ Science Knowledge and Skills. School Science and Mathematics, 113(5), 215−226. doi: 10.1111/ssm.12023 [30] Denney, A. S., Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to Write a Literature Review. Journal of Criminal Justice Education, 24(2), 218−234. doi: 10.1080/10511253.2012.730617 [31] Duval, S., & Tweedie, R. (2000). Trim and Fill: A Simple Funnel-Plot-Based Method of Testing and Adjusting for Publication Bias in Meta-Analysis. Biometrics, 56(2), 455−463. doi: 10.1111/j.0006-341X.2000.00455.x [32] Fan, S. C., & Yu, K. C. (2015). How an integrative STEM curriculum can benefit students in engineering design practices. International Journal of Technology & Design Education, 27(1), 1−23. [33] Fatade, A. O., Mogari, D., & Arigbabu, A. A. (2013). Effect of Problem-Based Learning on Senior Secondary School Students’ Achievements in Further Mathematics. Acta Didactica Napocensia, 6(3), 27−44. [34] Freeman, S., Eddy, S. L., McDonough, M., Smith, M. K., Okoroafor, N., Jordt, H., & Wenderoth, M. P. (2014). Active Learning Increases Student Performance in Science, Engineering, and Mathematics. National Acad Science, 111(23), 8410−8415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1319030111 [35] Han, S., Rosli, R., Capraro, M. M., & Capraro, R. M. (2016). The Effect of Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) Project Based Learning (PBL) on Students’ Achievement in Four Mathematics Topics. Journal of Turkish Science Education, 13, 3−29. doi: 10.12973/tused.10153a [36] Harris, C. J., Penuel, W. R., D’Angelo, C. M., DeBarger, A. H., Gallagher, L.P., Kennedy, C. A., Cheng, B. H., & Krajcik, J. S. (2015). Impact of Project-Based Curriculum Materials on Student Learning in Science: Results of a Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 52(10), 1362−1385. doi: 10.1002/tea.21263 [37] Holveck, S. E. (2012). Teaching for Conceptual Change in a Density Unit Taught to 7th Graders: Comparing Two Teaching Methodologies-Scientific Inquiry and a Traditional Approach. Oregon: University of Oregon. [38] Honey, M., Pearson, G., & Schweingruber, H. (2014). STEM Integration in K-12 Education Status, Prospects, and an Agenda for Research. Washington D. C.: National Academies Press. [39] James, J. S. (2014). Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) Curriculum and Seventh Grade Mathematics and Science Achievement. Michigan: ProQuest LLC. [40] Kalaian, S. A., & Kasim, R. M. (2014). A Meta-Analytic Review of Studies of the Effectiveness of Small-Group Learning Methods on Statistics Achievement. Journal of Statistics Education, 22(1), 1−20. [41] Kala. (2018). Effectiveness of Small-Group Learning Pedagogies in Engineering and Technology Education: A Meta-Analysis. Journal of Technology Education, 29(2), 20−35. doi: 10.21061/jte.v29i2.a.2 [42] Kassir, H. A. N. (2013). The effectiveness of the Science-Inquiry Teaching Approach on the Students’ Achievement and Engagement in the UAE’ Public Schools. Dubai: The British University in Dubai. [43] Kelley, T. R., & Knowles, J. G. (2016). A conceptual framework for integrated STEM education. International Journal of STEM Education, 3, 1−11. [44] Kim, K. H., Tassel-Baska, J. V., Bracken, B. A., Feng, A., Stambaugh, T., & Bland, L. (2012). Project Clarion: Three Years of Science Instruction in Title I Schools among K-Third Grade Students. Research in Science Education, 42(5), 813−829. doi: 10.1007/s11165-011-9218-5 [45] Kim, N. A., Belland, B. R., & Walker, A. E. (2018). Effectiveness of Computer-Based Scaffolding in the Context of Problem-Based Learning for Stem Education: Bayesian Meta-analysis. Educational Psychology Review, 30(2), 397−429. doi: 10.1007/s10648-017-9419-1 [46] Kine, M. S. (2017). Visual-Spatial Ability in STEM Education: Transforming Research into Practice. Switzerland: Springer International Publishing Switzerland, 2017. [47] Kizkapan, O., & Bektas, O. (2017). The Effect of Project Based Learning on Seventh Grade Students’ Academic Achievement. International Journal of Instruction, 10(1), 37−54. doi: 10.12973/iji.2017.1013a [48] Korur, F., Efe, G., Erdogan, F., & Tunc, B. (2015). Effects of Toy Crane Design-Based Learning on Simple Machines. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 15, 251−271. [49] Lazowski, R., & Hulleman, C. (2015). Motivation Interventions in Education: A Meta-Analytic Review. Review of Educational Research, 86(2), 1−39. [50] Li, Y., Huang, Z., Jiang, M., & Chang, T. W. (2016). The Effect on Pupils’ Science Performance and Problem-Solving Ability through Lego: An Engineering Design-based Modeling Approach. Educational Technology & Society, 19(3), 143−156. [51] Lipsey, M. W., & Wilson, D. B. (2001). Practical Meta-Analysis. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications, Inc. [52] Maxwell, D. O., Lambeth, D. T., & Cox, J. T. (2015). Effects of Using Inquiry-Based Learning on Science Achievement for Fifth-Grade Students. Asia-Pacific Forum on Science Learning and Teaching, 16(1), 1−31. [53] McDonald, C. V. (2016). STEM Education: A Review of the Contribution of the Disciplines of Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics. Science Education International, 27(4), 530−569. [54] Merrill, C. (2001). Integrated Technology, Mathematics, and Science Education: A Quasi-Experiment. Journal of Industrial Teacher Education, 38, 45−61. [55] Michko, G. M. (2008). Meta-Analysis of Effectiveness of Technology Use in Undergraduate Engineering Education. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/224361059_Meta-analysis_of_effectiveness_of_technology_use_in_undergraduate_engineering_education. [56] Ojaleye, O., & Awofala, A. O. A. (2018). Blended Learning and Problem-Based Learning Instructional Strategies as Determinants of Senior Secondary School Students’ Achievement in Algebra. International Journal of Research in Education and Science, 4(2), 486−501. [57] Olivarez, N. (2013). The Impact of a STEM Program on Academic Achievement of Eighth Grade Students in a South Texas Middle School. Corpus Christi, Texas: Texas A & M University - Corpus Christi. [58] Rehmat, A. P. (2015). Engineering the Path to Higher-Order Thinking in Elementary Education: A Problem-Based Learning Approach for STEM Integration. Las Vegas: University of Nevada. [59] Robinson, A., Dailey, D., Hughes, G., & Cotabish, A. (2014). The Effects of a Science- Focused STEM Intervention on Gifted Elementary Students’ Science Knowledge and Skills. Journal of Advanced Academics, 25(3), 189−213. doi: 10.1177/1932202X14533799 [60] Rosenthal, R. (1979). The “File Drawer Problem” and Tolerance for Null Results. Psychol Bull, 86, 638−641. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.86.3.638 [61] Rothstein, H. R., Sutton, A. J., & Borenstein, M. (2005). Publication Bias in Meta-Analysis Prevention, Assessment and Adjustments.Chichester: John Wiley & Sons Ltd. [62] Rozek, C. S., Ramirez, G., Fine, R. D., & Beilock, S. L. (2019). Reducing Socioeconomic Disparities in the STEM Pipeline Through Student Emotion Regulation. Proceeding of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 116(5), 1553−1558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1808589116 [63] Sanders, M. (2009). STEM, STEM Education, STEMmania. Technology Teacher, 68(4), 20−26. [64] Sarac, H. (2018). The Effect of Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics-Stem Education Practices on Students’ Learning Outcomes: A meta-analysis. The Turkey Online Journal of Educational Technology, 17(2), 125−142. [65] Slavin, R. E. (2008). Evidence-Based Reform in Education: What Will It Take?. European Educational Research Journal, 7(1), 124−128. doi: 10.2304/eerj.2008.7.1.124 [66] Slavin, R. E. (2017). Evidence-Based Reform in Education. Journal of Education for Students Placed at Risk, 22(3), 178−184. doi: 10.1080/10824669.2017.1334560 [67] Sokolowski, A. (2013). The Effects of Exploratory Learning Environments on Students’ Mathematics Achievement. Texas: Texas A&M University. [68] Sokolowski, A., Li, P., & Willson, V. (2015). The Effects of Using Exploratory Computerized Environments in Grades 1 to 8 Mathematics: A Meta-Analysis of Research. International Journal of STEM Education, 2(8), 1−17. [69] Steenbergen-Hu, S., & Cooper, H. (2013). A Meta-Analysis of the Effectiveness of Intelligent Tutoring Systems on K-12 Students’ Mathematical Learning. Journal of Educational Psychology, 105(4), 970−987. doi: 10.1037/a0032447 [70] Taylor, K. (2016). Collaborative Robotics, More Than Just Working in Groups: Effects of Student Collaboration on Learning Motivation, Collaborative Problem Solving, and Science Process Skills in Robotic Activities. Boise: Boise State University. [71] Valentine, J. C., & Cooper, H. (2003). What Works Clearinghouse Study Design and Implementation Assessment Device (Version 0.6). Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Education. [72] Yasin, R. M., & Yunus, N. S. (2014). A Meta-Analysis Study on the Effectiveness of Creativity Approaches in Technology and Engineering Education. Asian Social Science, 10(3), 242−252. [73] Yildirim, B. (2016). An Analyses and Meta-Synthesis of Research on STEM Education. Journal of Education and Practice, 7(34), 23−33. [74] Young, J., Ortiz, N., & Young, J. (2017). STEMulating Interest: A Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Out-of-School Time on Student STEM Interest. International Journal of Education in Mathematics, Science and Technology, 5(1), 62−74. [75] Zeng, Z., Yao, J. Gu, H., & Przybylski, R. (2018). A Meta-Analysis on the Effects of STEM Education on Students’ Abilities. Science Insights Education Frontiers, 1(1), 3−16. doi: 10.15354/sief.18.re005 -





 下载:
下载: